Optical Switch
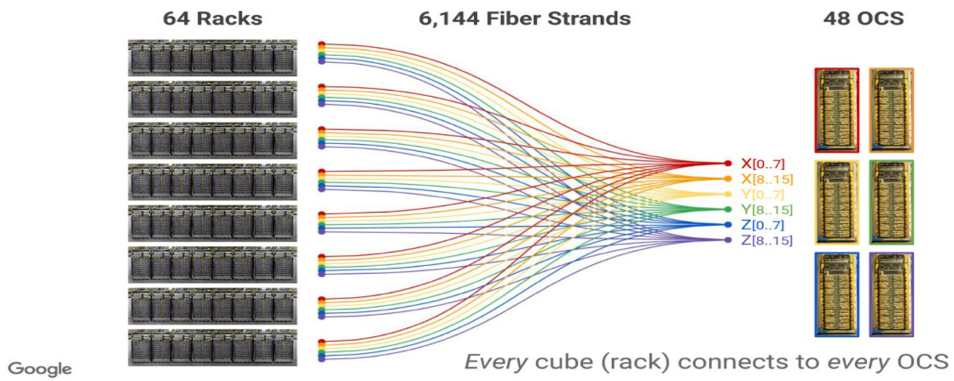
Google’s Optical Circuit Switch
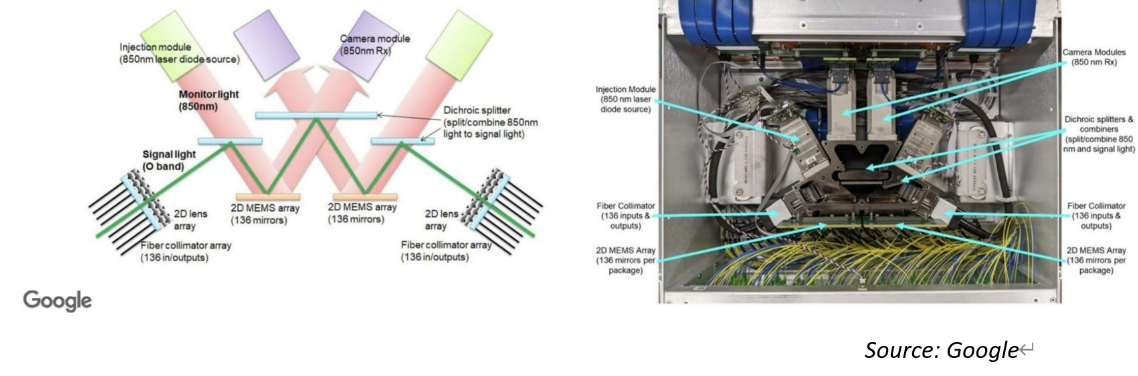
Optical Circuit Switching (OCS) is a networking technology that uses optical signals to create dedicated communication paths or "circuits" between nodes. Unlike traditional packet switching, where data is broken into packets and sent separately, OCS establishes a direct, continuous connection for the duration of the communication session.
In an Optical Circuit Switch, the switching is done using optical components such as mirrors or lenses, allowing data to be transmitted without the need for electronic-to-optical conversion at each switch. This technology can provide low-latency and high-throughput communication, making it suitable for certain applications, especially in scenarios where predictable, dedicated connections are required.
(Optical Circuit Switching (OCS) is a networking tech that uses light signals to create direct communication paths between devices, unlike breaking data into packets. In OCS, switches use optical tools like mirrors, skipping the need for converting signals between electronics and optics at each switch,offering quick and efficient communication without delays.)
OCS is optically reconfigurable AI network as it has achieved better performance, lower power, and more flexibility. It has been in production for years. For the fiber connection It has over 16,000 connections and enough distance of fiber in the super pod.
OCS (Optical Circuit Switching) brings various advantages with its unique network technology architecture. Firstly, by establishing direct communication paths, OCS achieves low-latency transmission, eliminating the waiting time for data packet transfer in traditional packet switching, thereby improving communication speed. Secondly, OCS supports high-bandwidth communication by transmitting data through dedicated connections, effectively enhancing data transfer rates. This makes it an ideal choice for handling large-scale data and high-performance computing tasks.
PHOTONIC Connected XPU/SWITCH/HBM
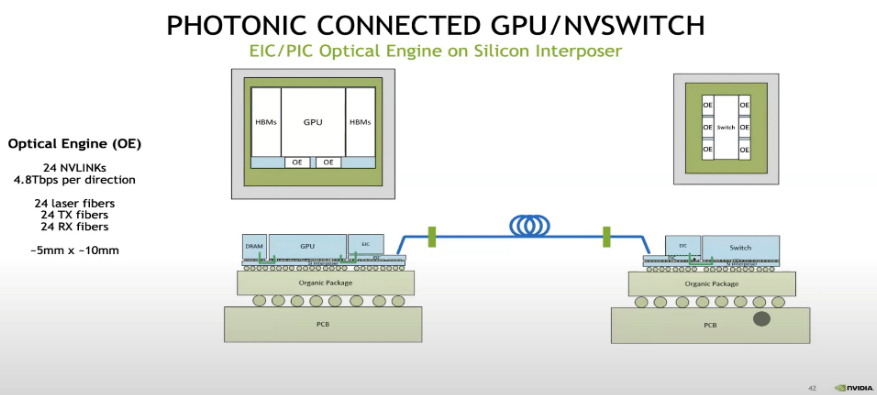
Nvidia’s Chief scientist Bill Dally presented the PHOTONIC Connected GPU/NVSWITCH at OFC 2022 which jumps ahead to what some future GPU accelerated system might look like with silicon photonics interconnect.
There are 24 fibers coming off each Optical Engine, and they initially would run at 200 Gb/sec signaling rates, for a combined 4.8 Tb/sec of bandwidth. Each GPU has a pair of these to give it bi-directional bandwidth into and out of an NVSwitch fabric. A NVSwitch with six optical engines would therefore be rated at 28.8 Tb/sec raw and 25.6 Tb/sec after encoding overhead is taken off.
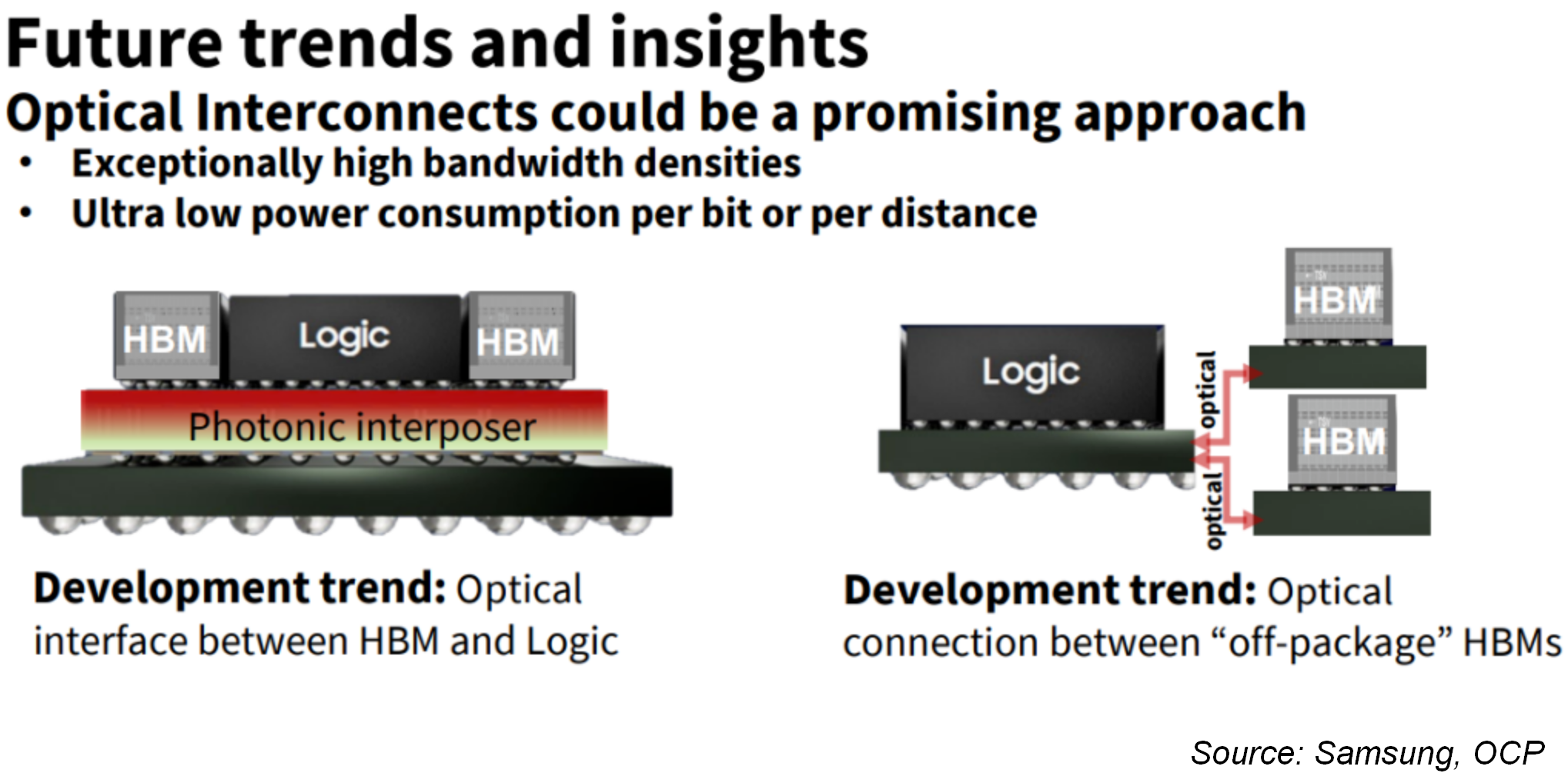
At 2023's Open Compute Project (OCP) Global Summit, Samsung's Advanced Packaging Team Yan Li presented us with a glance at a more integrated future than we might expect: one where thermal and transistor density issues with further High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) development could be solved through photonics. This simplifies chip manufacturing and packaging costs for both HBM and logic and does away with complex, in-circuitry, local conversion from digital to optical.
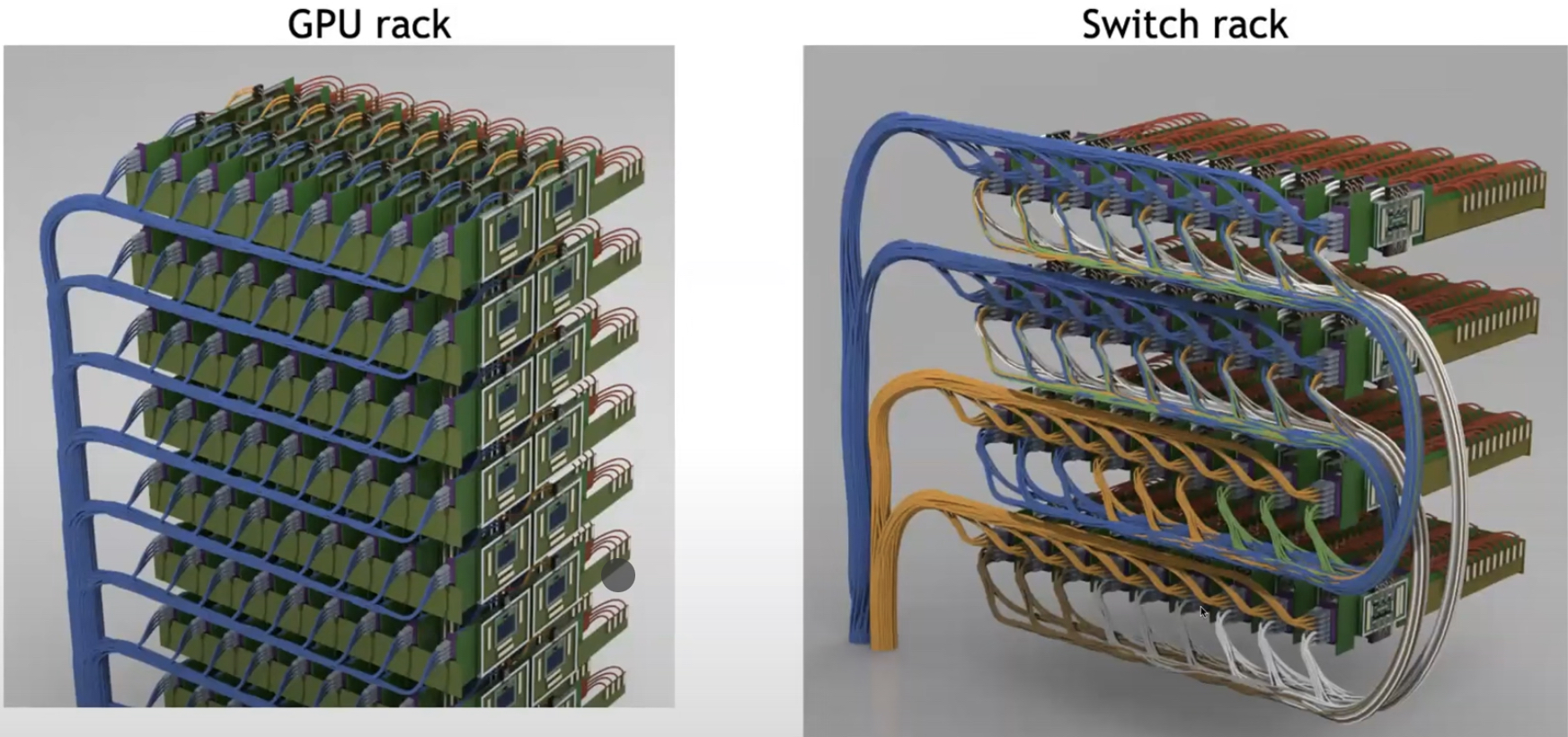
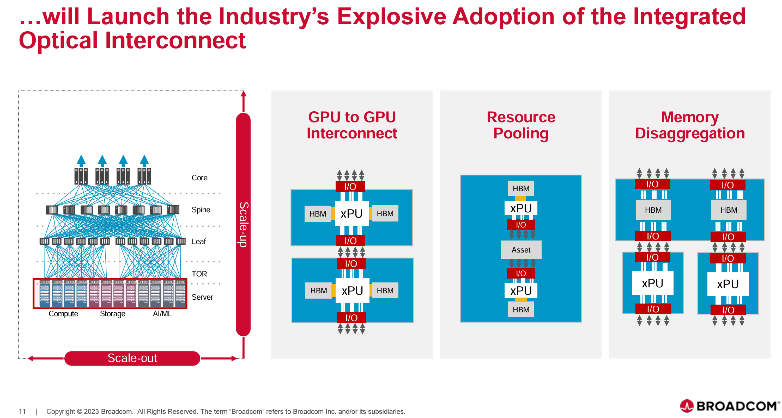
There is also a paper from Broadcom shows the concept of GPU interconnect and to the HBM connection, showcasing a sophisticated approach to data transfer within systems. Particularly, the paper highlights the integration of fiber optic solutions in facilitating these connections. It underscores the significance of optical fiber technology in enabling high-speed and efficient communication between graphics processing units (GPU) and high bandwidth memory (HBM), emphasizing the need for advanced solutions to meet the demands of computing environments.
Copyright © Samba Labs
Fast Navigation
—